Kehutanan UNISMUH Makassar - Forestry Education and Forest Monitoring Platform
Platform Status: All Systems Operational
Educational Forest Monitoring System will send alerts automatically when there is Grid on Medium+ Fire Risk or LST > 38°C or Grid has Poor vegetation healthVegetation Health Satellite Monitoring
Forest Fire Detection
VIIRS Real-time MonitoringCam 1 Temporary Disconnected
Cam 2 Temporary Disconnected
Grid Monitoring Vegetation Health Map

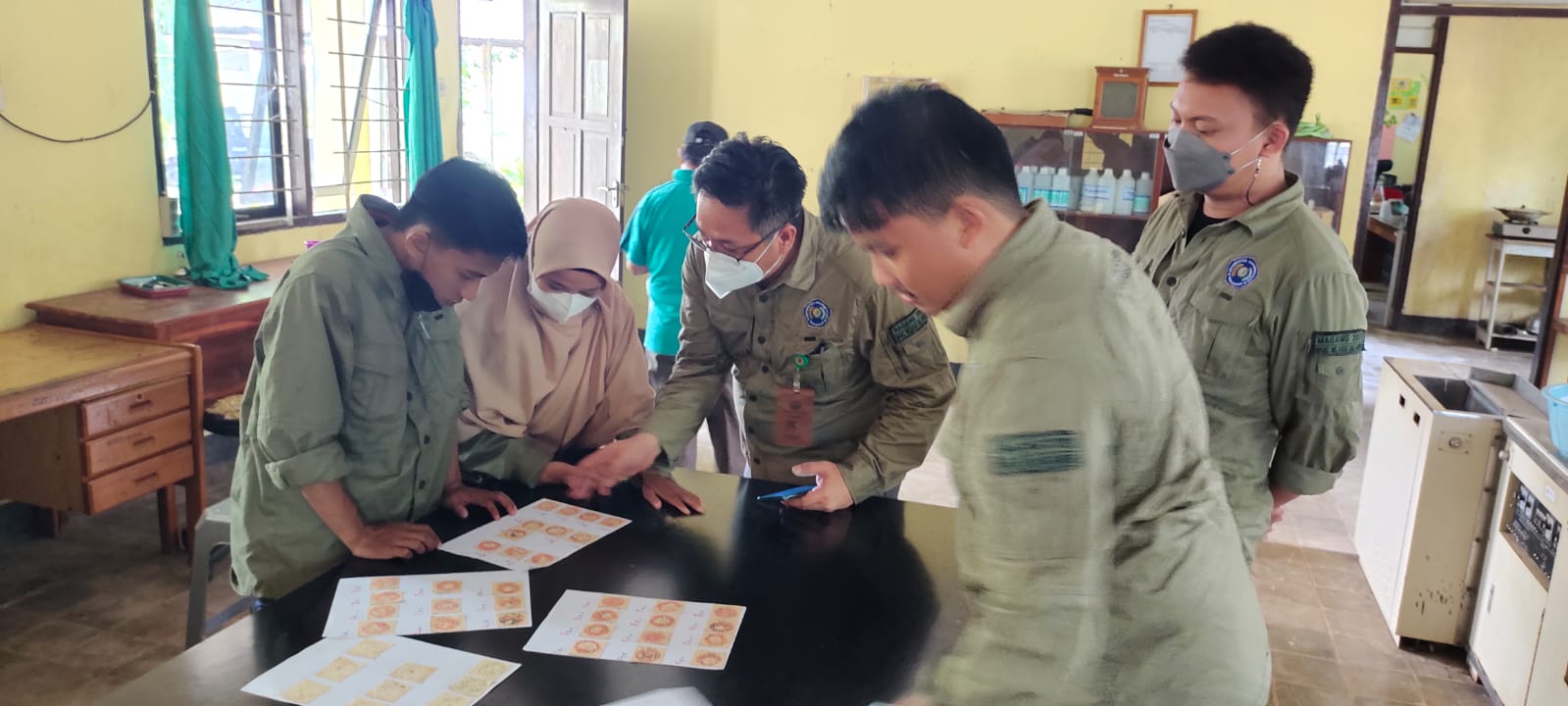
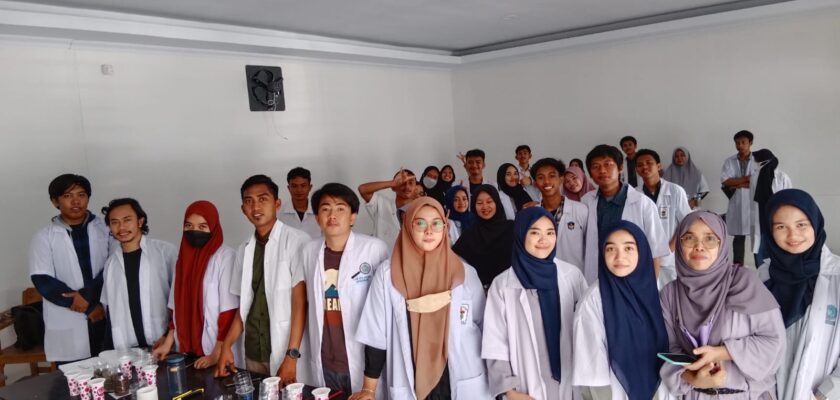
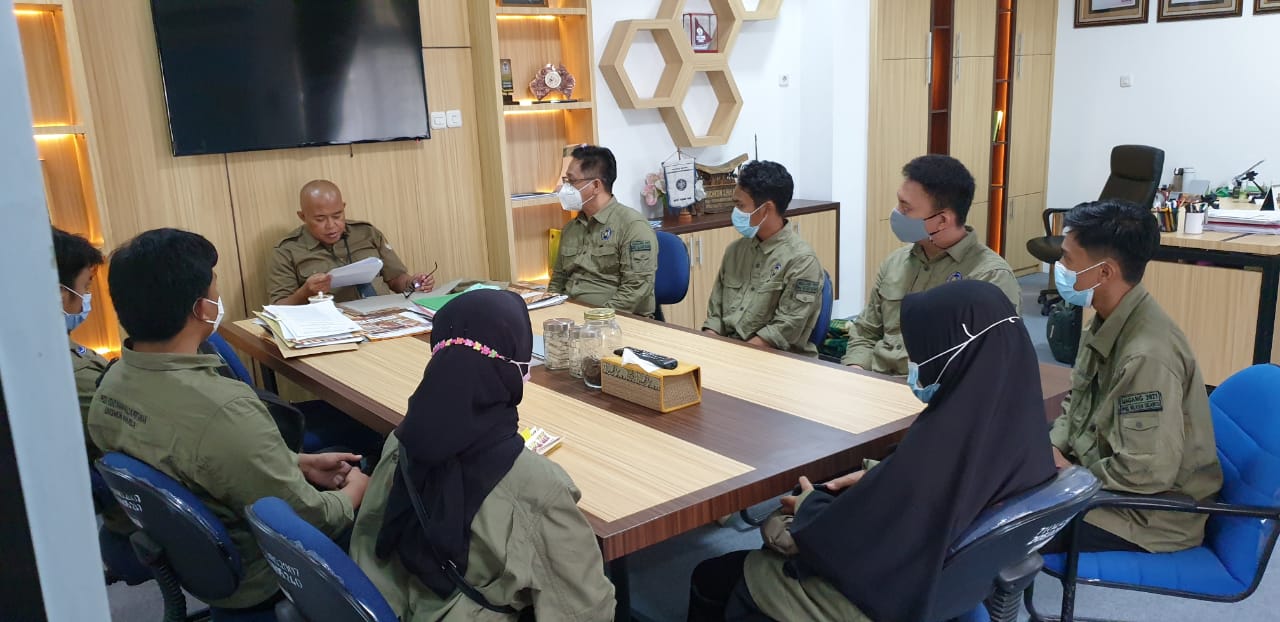
Pembekalan Magang Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Tekankan Profesionalisme di Berbagai Lembaga Kehutanan
Pembekalan Magang Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Tekankan Profesionalisme di Berbagai Lembaga Kehutanan
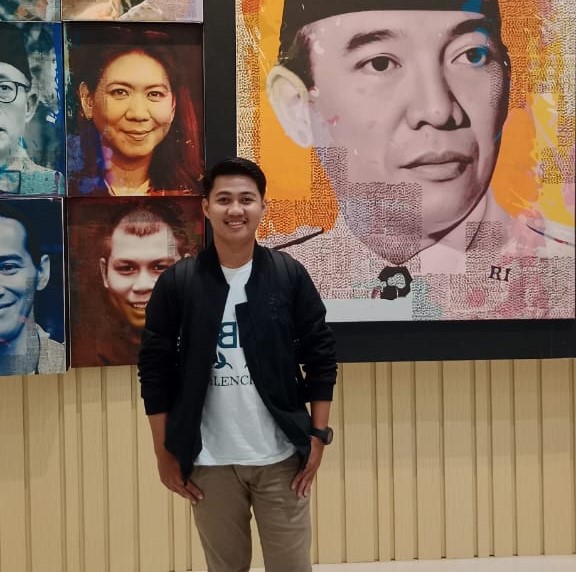

Dosen Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Raih Bantuan Publikasi Jurnal Bereputasi Tahun 2025
Dosen Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Raih Bantuan Publikasi Jurnal Bereputasi Tahun 2025

Dosen Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Raih Penghargaan pada Kemahasiswaan Award 2025
Dosen Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar Raih Penghargaan pada Kemahasiswaan Award 2025
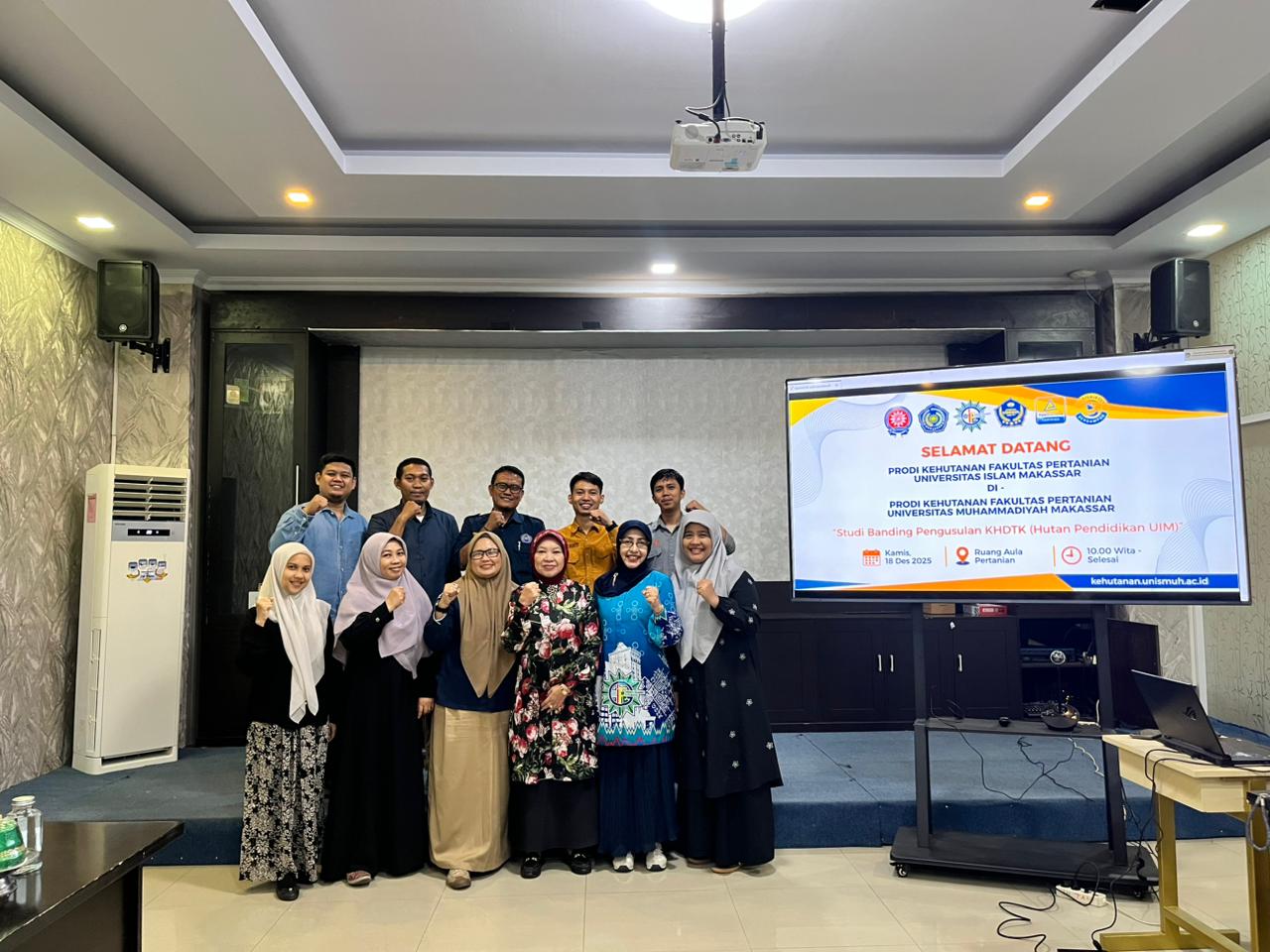

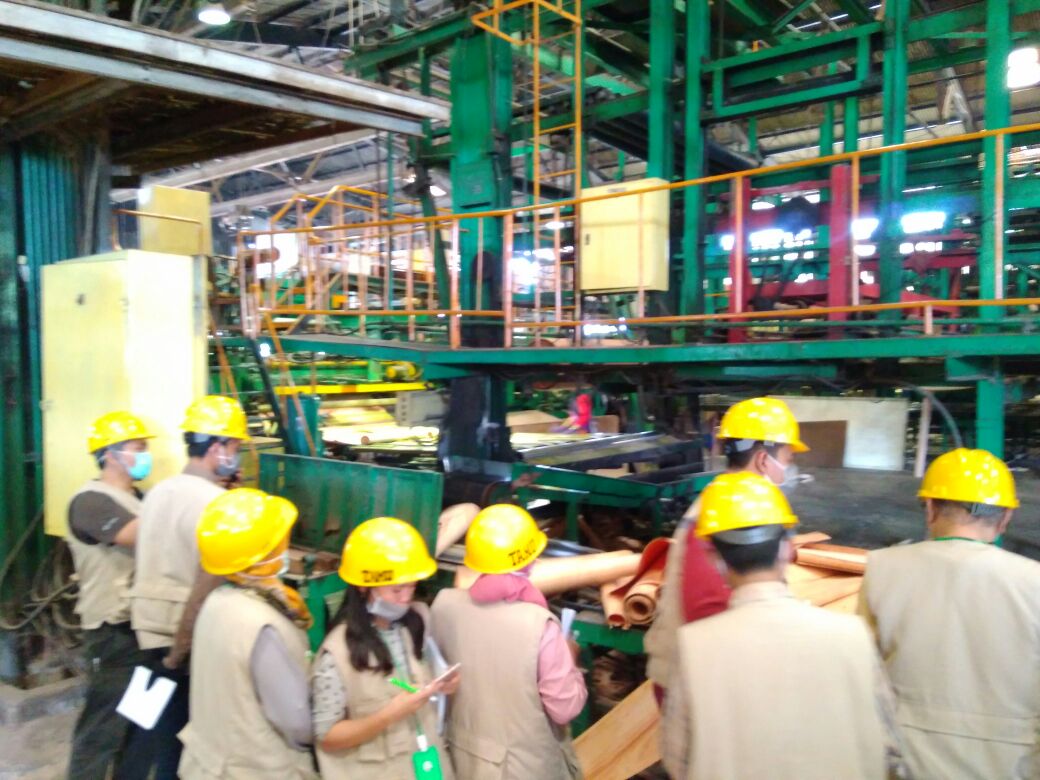
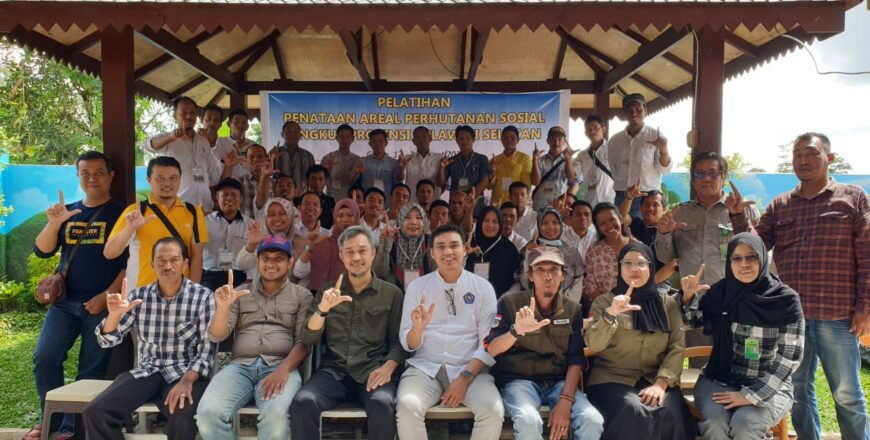
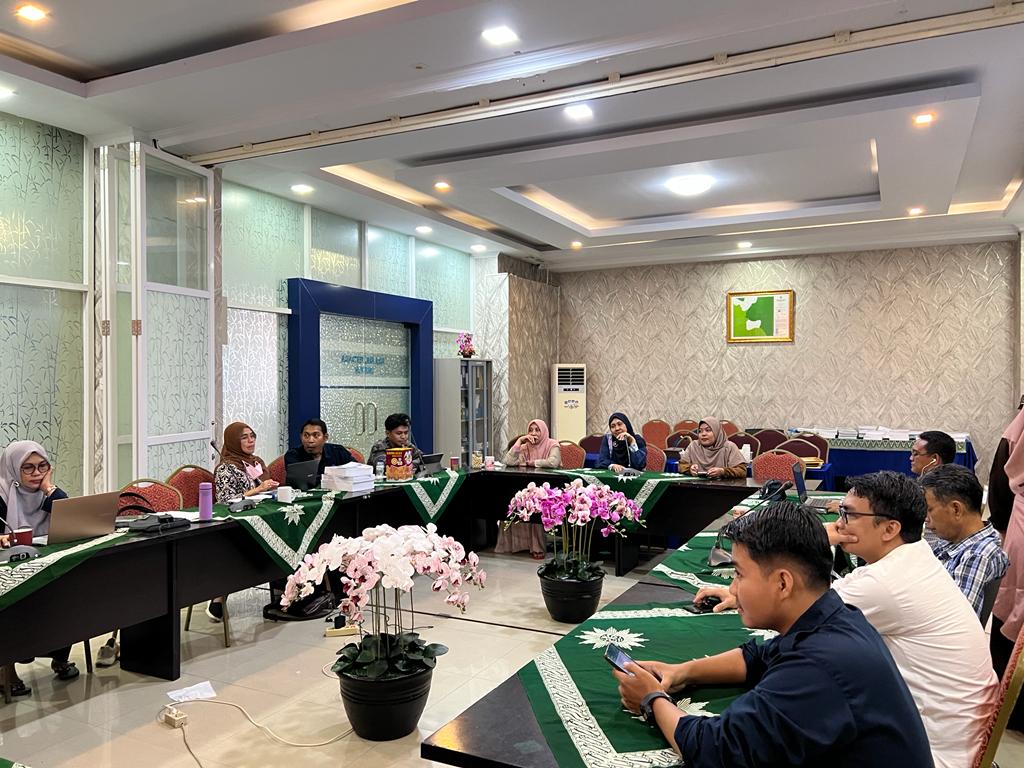
Prodi Kehutanan UIM Makassar Lakukan Studi Banding Pengembangan KHDTK ke Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar
Prodi Kehutanan UIM MakassarLakukan Studi Banding Pengembangan KHDTK ke Prodi Kehutanan Unismuh Makassar
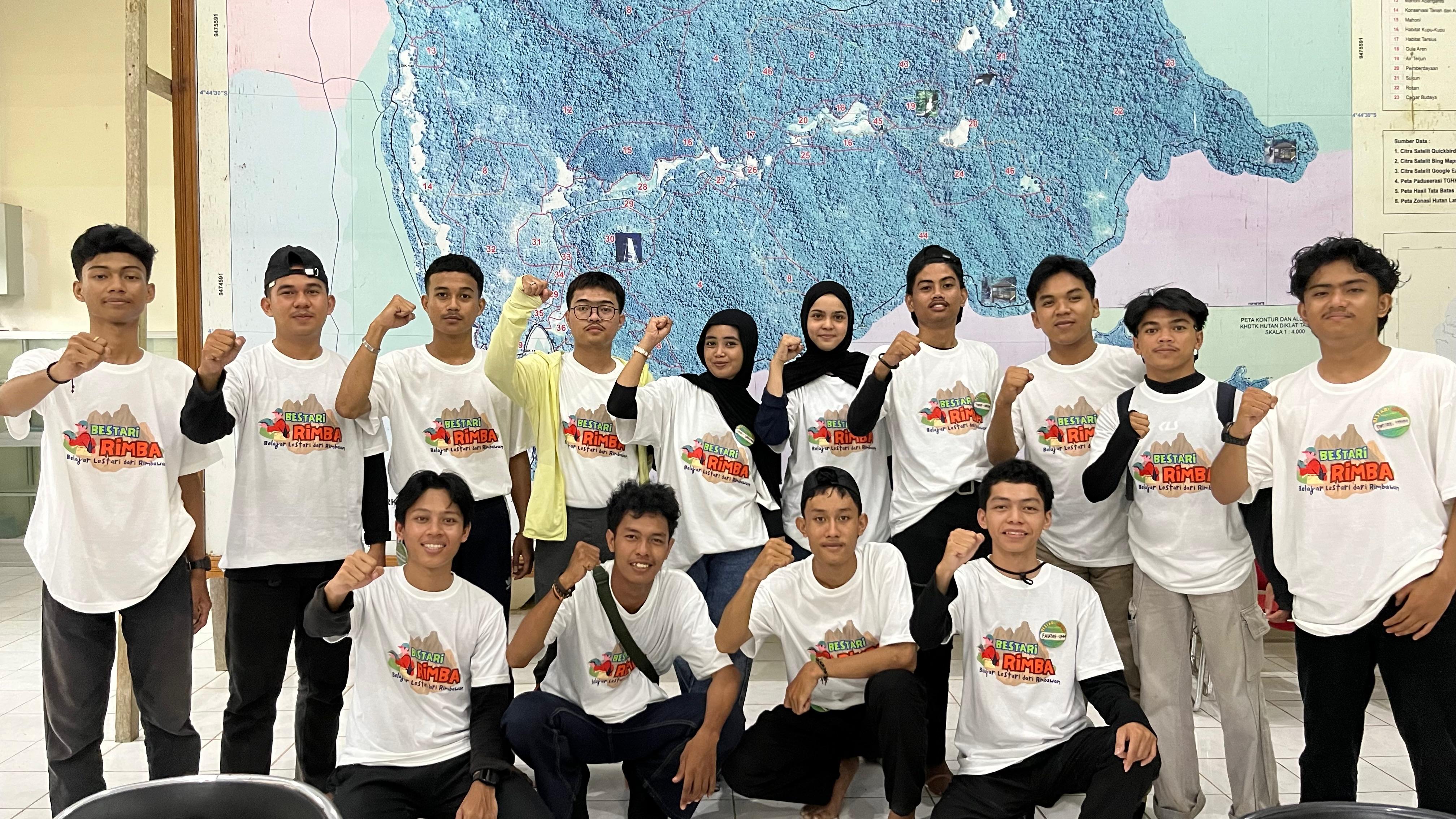

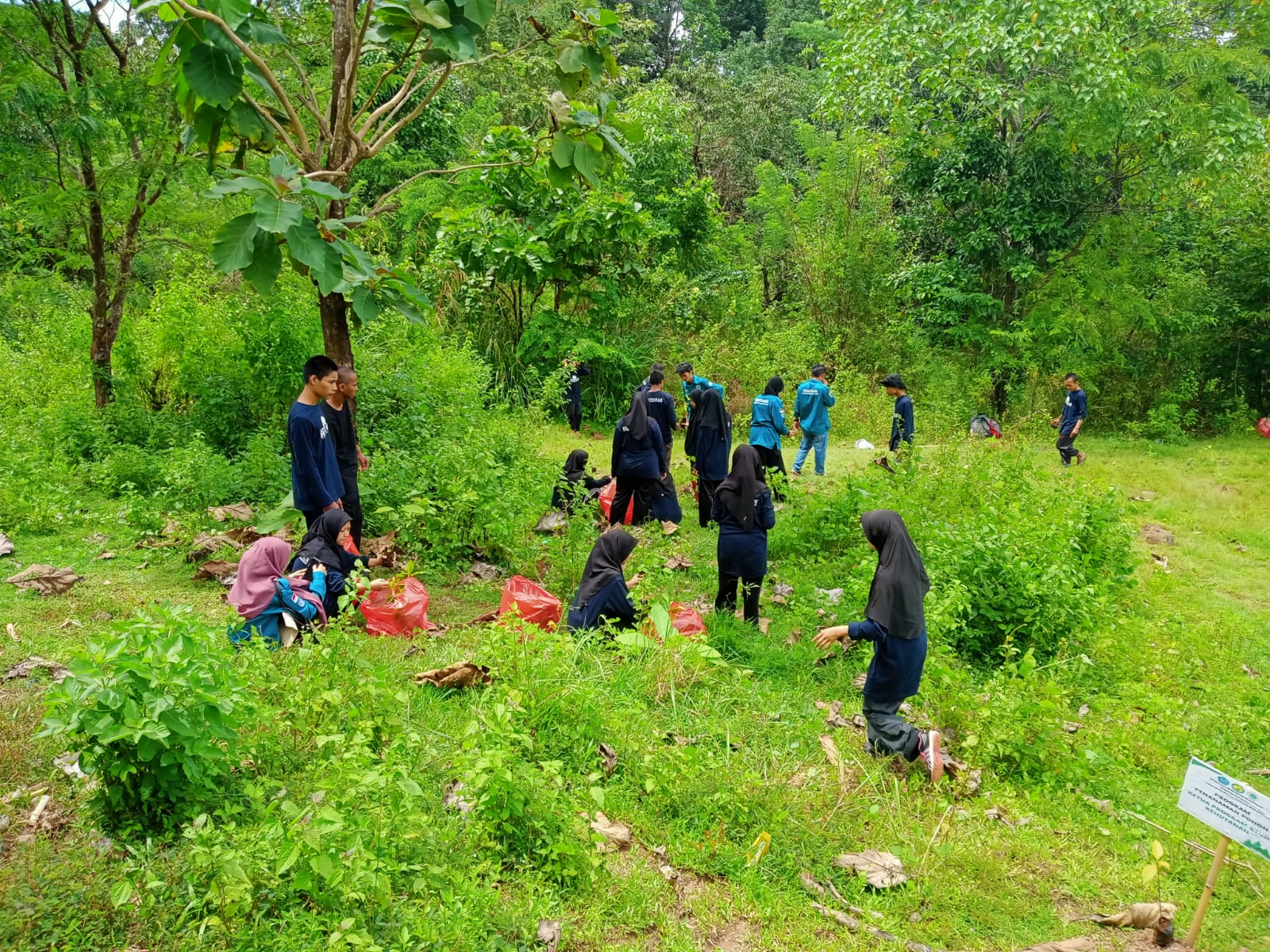
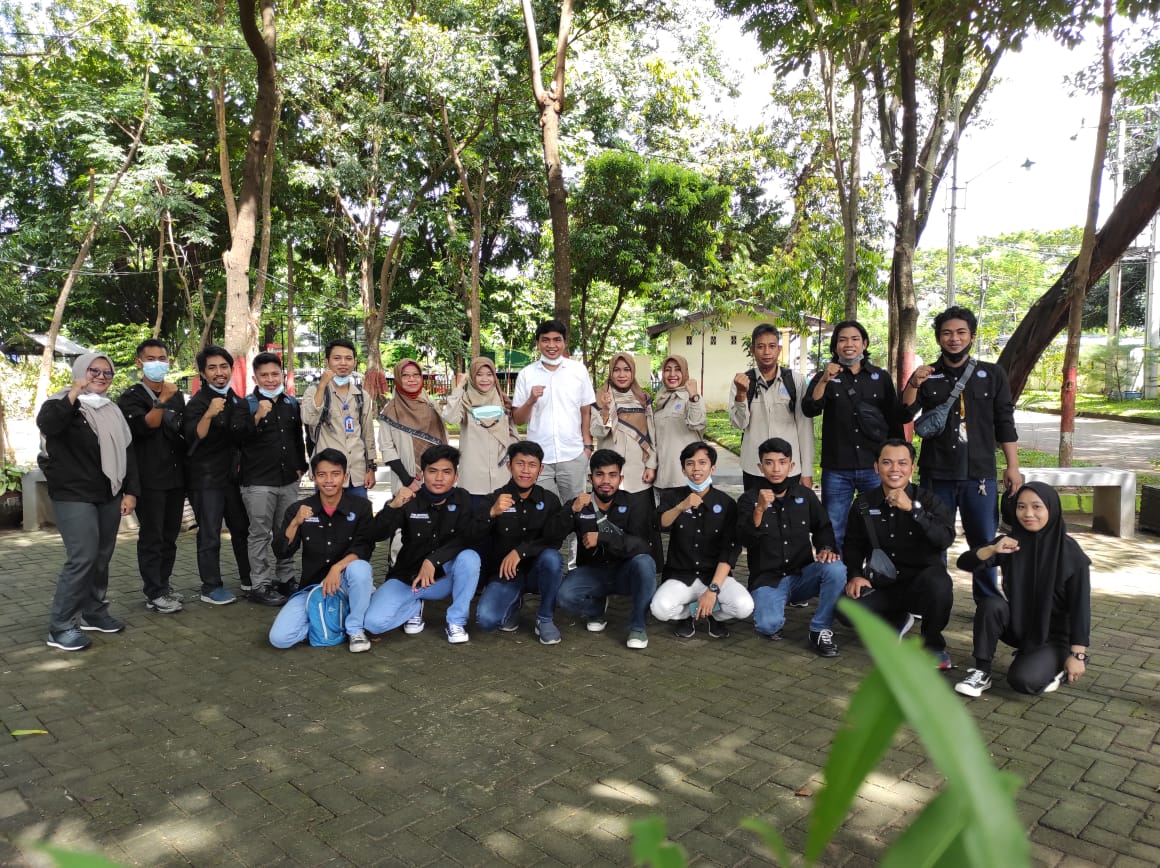
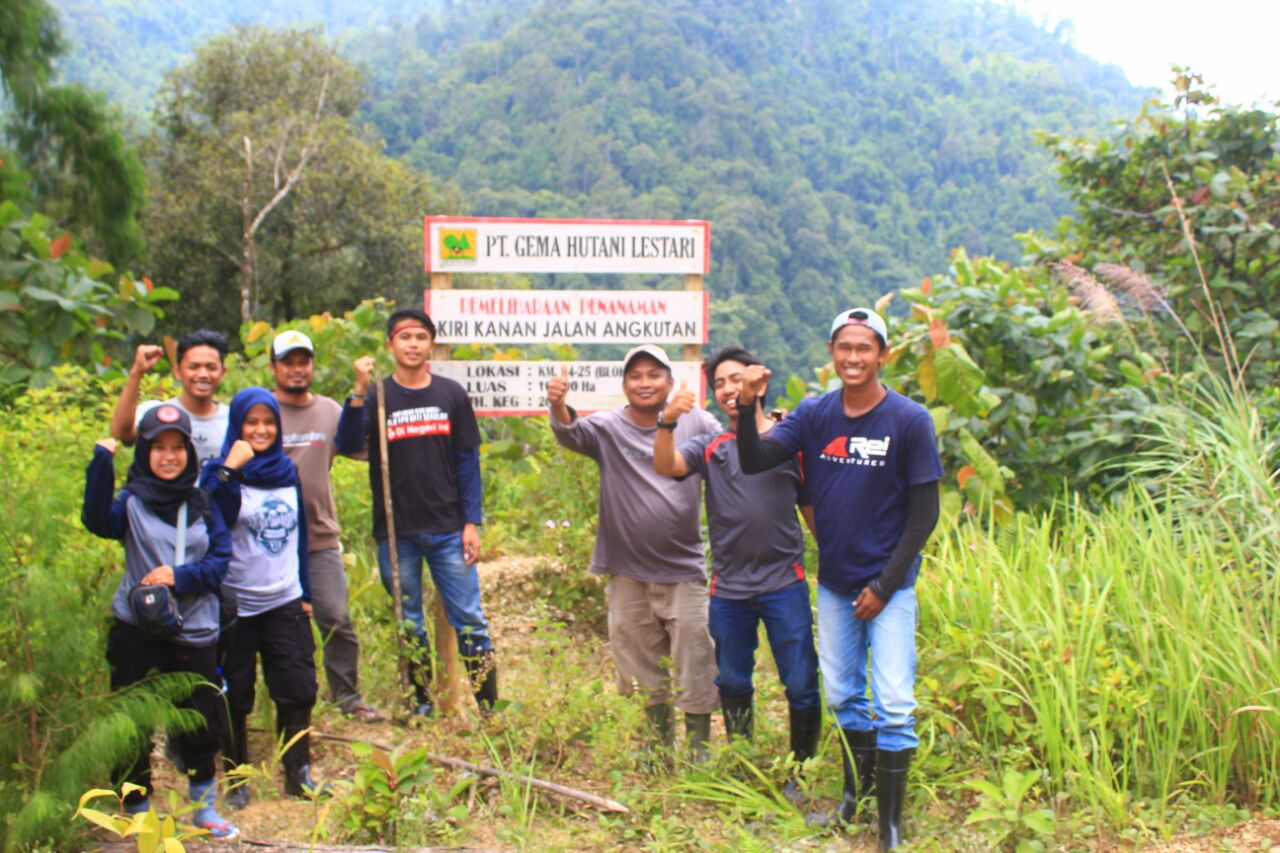
Mahasiswa Unismuh Makassar Ikuti Program BESTARI RIMBA: Eksplorasi Hutan dan Pendidikan Lingkungan
Mahasiswa Unismuh Makassar Ikuti Program BESTARI RIMBA: Eksplorasi Hutan dan Pendidikan Lingkungan
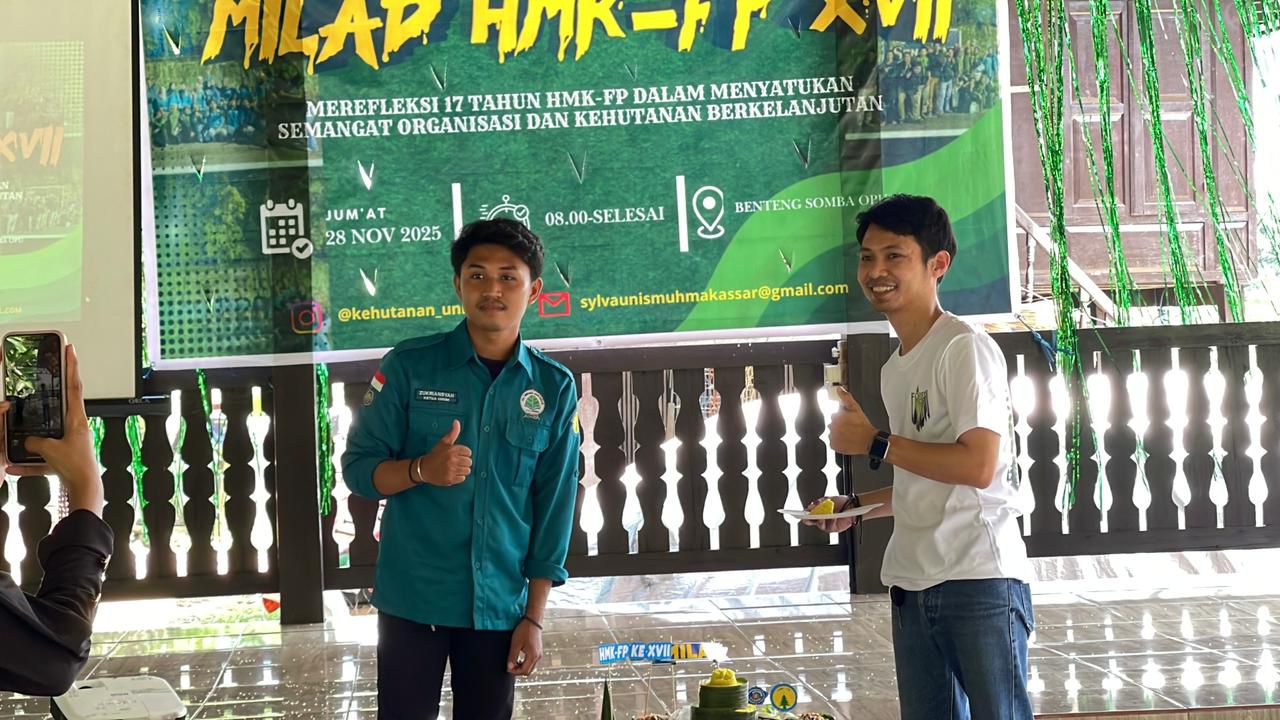

HMK-FP Unismuh Makassar Peringati Milad ke-17: Momentum Refleksi dan Penguatan Komitmen Kehutanan Berkelanjutan
HMK-FP Unismuh Makassar Peringati Milad ke-17: Momentum Refleksi dan Penguatan Komitmen Kehutanan Berkelanjutan



















Recent Activities
Categories
Research
(45)Field Work
(32)Training
(28)Conservation
(25)Drone Tech
(18)Publications
(15)Popular Tags
Quick Stats
Our Journals
Theme Customization






 WASIAN
WASIAN
 FORCES
FORCES